Cancer can be a terrifying word, and the thought of stuff diagnosed with it can be overwhelming. However, the good news is that many types of cancer can be detected early through regular screening tests. The question is, when should you start getting screened? And which screening tests are weightier for men and women? These are crucial questions that every individual should consider. In this blog, we’ll swoop into the latest recommendations for cancer screenings for men and women, and explore the weightier age to start getting screened. By the end, you’ll have a largest understanding of what you can do to modernize your chances of detecting cancer early and ultimately, improving your chances of survival.
Screening Tests for Women:
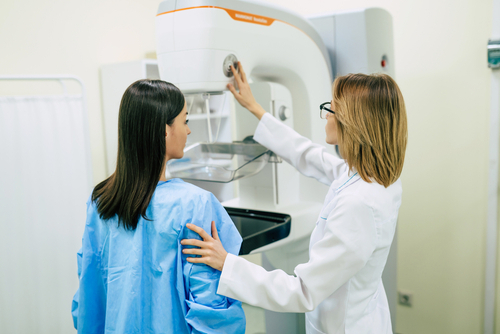
Breast Cancer:
Mammography is the primary screening test for detecting breast cancer. Women with an stereotype risk of breast cancer should start getting mammograms at age 45 and protract to get them annually until age 54. Without age 54, women can segregate to protract getting yearly mammograms (only if they are healthy enough) or switch to getting them every two years. However, women between 40 and 44 moreover have the option to start screening once a year. Women who are at an elevated risk of breast cancer, such as those with a family history of the disease, may require older or increasingly frequent mammogram screenings.

Mammography
Other Promising Breast Cancer Screening Technologies:
Breast MRI is a new technology that is stuff studied for use in women with a higher risk of breast cancer. It is currently recommended as a supplementary screening tool for women who are at upper risk of developing breast cancer. Ultrasound is moreover stuff researched as a potential volitional for women who are unable to undergo a mammogram. However, both these technologies are still stuff evaluated for their effectiveness in detecting breast cancer, and women should discuss their risk factors with their healthcare provider to determine the most towardly screening method for them.
Cervical Cancer:
Pap tests and HPV DNA tests are both misogynist for cervical cancer screening. Additionally, colposcopy is flipside option for examining the cervix visually. This simple test entails using a colposcope, a specialized instrument, to examine the cervix and vagina for any abnormalities. If any unusual findings are observed during the exam, a biopsy may moreover be performed.
Women can start getting Pap tests at age 21 and protract to get them every three years until age 29. Without age 30, women can segregate to get a Pap test every three years, or a combination of a Pap test and an HPV test every five years, and protract to get screened until age 65 or 70. The HPV test is recommended for women weather-beaten 30 and over, and it’s usually washed-up every five years withal with a Pap test. If a woman has an unwont Pap test, she may moreover be tested for HPV. Women who have had a hysterectomy may not need regular Pap tests. Women who have a higher risk of cervical cancer may need to get screened increasingly wontedly or start screening at an older age.
Know the link between HPA and Cervical Cancer
Ovarian Cancer:
There is no standard screening test for ovarian cancer, but women who have a family history of ovarian or breast cancer may need to have a transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) and a CA-125 thoroughbred test. TVUS utilizes sound waves to produce images of the ovaries, which can help identify potential abnormalities in high-risk women. However, it is not recommended for women at stereotype risk considering it can result in false-positive results. On the other hand, the CA-125 thoroughbred test measures the levels of CA-125 protein in the blood, which may increase in the specimen of ovarian cancer. However, this test is not recommended for screening considering it can produce false-positive results, particularly in premenopausal women.
Women with an elevated risk of ovarian cancer, mainly with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations may consider removing their ovaries and fallopian tubes without completing childbearing to reduce their risk of ovarian cancer.
Screening Tests for Men:
Prostate Cancer:
There is no standard test for prostate cancer screening. However, two tests are wontedly recommended, such as Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) test and Digital Rectal Viewing (DRE). The PSA test is a thoroughbred test that measures the level of PSA in the blood, and elevated levels may indicate the presence of prostate cancer. The DRE involves a healthcare provider inserting a gloved and lubricated finger into the rectum to trammels for any abnormalities in the prostate.
Men with stereotype risk should talk to their doctor well-nigh whether or not to have a PSA thoroughbred test starting at age 50. Men between the month of 60 and 70, who are at higher risk of prostate cancer, can undergo a prostate viewing and have a serum PSA test once a year. Men with a family history of prostate cancer may need to start screening earlier.
Screening Tests For Both Men & Women:
Colorectal Cancer:
When it comes to screening for colorectal cancer, colonoscopy and stool tests are the primary methods recommended. For those at stereotype risk, regular colonoscopies once every 10 years should uncork at age 45 and protract until the age of 75 (only if healthy unbearable and expected to live at least 10 increasingly years). In between colonoscopies or for those unable to undergo colonoscopy, stool tests may be washed-up once a year. For individuals between the month of 76 and 85, the visualization to protract screening should be made with their doctor based on personal preferences, prior screening results, overall health, and life expectancy. Those over 85 should no longer be screened for colorectal cancer.
However, individuals with higher risk factors should uncork screening surpassing the age of 45. Higher risk factors include:
- Strong family history of colorectal cancer or unrepealable types of polyps
- Personal history of colorectal cancer or unrepealable types of polyps
- Inflammatory exenterate disease
- Family history of hereditary syndromes such as FAP or Lynch syndrome
- History of radiation therapy to the stomach or pelvis
In wing to colonoscopy and stool tests, other screening options include CT colonography and flexible sigmoidoscopy, which should be washed-up once every 5 years.
Oral Cancer:
Currently, there is no standard screening test for oral cancer. However, individuals who are at higher risk for oral cancer, such as those who use tobacco products, slosh swig regularly or have a family history of oral cancer, may goody from frequent oral cancer screening by visiting a dentist or an ENT specialist once a year. Screening tests for oral cancer typically involve a visual and physical exam of the mouth and throat by a healthcare provider. During the exam, the provider will squint for any signs of unwont growth or tissue changes, such as sores, lumps, or discolouration. They may moreover finger for any lumps or abnormalities in the neck, as some types of oral cancer can spread to the lymph nodes.
In wing to a physical exam, some healthcare providers may use special tools or techniques to aid in oral cancer screening. For example, the provider may use a special light or dye to largest visualize any unwont areas in the mouth, or they may perform a skim biopsy to collect cells from suspicious areas for remoter testing. It helps snift tumored or pre-cancerous lesions early.
Lung Cancer:
Lung cancer lacks a standard screening test, but individuals at upper risks, such as smokers or those with other risk factors, may goody from yearly low-dose CT (LDCT) scans of the chest. This screening is recommended once a year for people between 50 to 80 years old, and in good health. It is expressly salubrious to those who currently smoke or quit smoking within the past 15 years, or those with a smoking history of 1 pack a day. However, screening is not suggested for individuals with lung cancer symptoms like coughing up thoroughbred or unexplained weight loss.
Liver Cancer:
The main tools for liver cancer screening are an ultrasound of the stomach withal with an alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) thoroughbred test. People who have upper swig consumption habits or infections such as hepatitis B & C have upper chances of liver damage, tabbed liver cirrhosis, leading to an increased risk of liver cancer. Therefore, individuals with chronic hepatitis B and C, cirrhosis, and a family history of liver cancer should be screened every six months with an ultrasound and AFP thoroughbred test.
Stomach Cancer:
Stomach cancer screening is not recommended for the unstipulated population, but those with a strong family history of stomach cancer or specific gastric diseases may goody from screening. Endoscopy is recommended once a year for some individuals, but not for everyone, for stomach cancer screening.
It’s important to note that these recommendations are unstipulated guidelines and may vary depending on individual risk factors. It’s unchangingly weightier to talk to your doctor well-nigh when to start getting screened and which tests are towardly for you. In wing to regular cancer screening tests, there are other things you can do to reduce your risk of cancer, such as quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and limiting your swig intake.
Related Articles:
10 Proven Ways to Prevent Oral Cancer
Cancer Screening: Should I Get Screened Or Not?
6 Alarming Signs of Gynaecological Cancers
Find Out Your Risk of Inheriting Cancer & Ways to Prevent it.
The post When Should You Start Getting Cancer Screenings? A Guide for Men and Women appeared first on Onco blog.
Related Post
 24
24 Sep
The Effects of Aging on Brain Function and Mental Health
Synopsis: The brain evolves as we get older. The effects of aging on brain is something that we should not take lightly. There are those individuals who might experience slight episodes of memory lapse and those who might experience severe.
Read More 15
15 Sep
Health Tips for Heart Health: Expert Guide to a Stronger Heart
Your heart is the motor of your body, working energetically to pump blood and oxygen all through your framework. However, heart malady remains one of the driving causes of passing around the world. The great news is that numerous heart.
Read More 29
29 Aug
Advanced Cancer Stages and Survival Rates
Progressed cancer alludes to stages where the illness has spread past its unique location, making treatment more challenging. Regularly, these incorporate Arrange 3 and Organize 4 cancer, regularly alluded to as late-stage or metastatic cancer. Stage 3 Cancer: Shows that cancer has.
Read More 21
21 Aug
Skin Allergies and Their Connection to the Immune System
Today, millions of people around the world are suffering from skin sensitivities, which is one of the most common dermatologist diagnosed conditions. They can present themselves as rashes, redness, hives, itching and inflammation or itching intensely. But past the unmistakable.
Read More